The cradle of civilization, Mesopotamia, stands as the venerable birthplace of numerous groundbreaking innovations and discoveries that have left an indelible mark on the course of human history. This ancient region, nestled between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, boasts a rich tapestry woven with threads of ingenuity and intellectual prowess. In this article, I am going to talk about the inventions of Mesopotamia, hope you will love this list of inventions of Mesopotamia.
In the annals of human achievement, the inventions emanating from Mesopotamia continue to resonate as evergreen pillars of inspiration. These pioneering contributions span a spectrum of fields, encompassing science, technology, and various facets of human progress. From the arcane mysteries of cuneiform writing to the complex machinations of early urban planning, the legacies of Mesopotamian ingenuity echo through the corridors of time.
Thriving Amidst the Sands of Time: Mesopotamian Science Unveiled
Delving deeper into the historical tapestry, Mesopotamian science, innovation, and technology experienced a zenith during the Uruk Period, a period dating back to 4100-2900 BCE. This golden epoch, characterized by remarkable cultural and societal advancements, laid the foundation for the flourishing of intellectual pursuits.
The vibrancy of Mesopotamian scientific inquiry manifested in diverse fields, ranging from astronomy and mathematics to medicine and agriculture. The Sumerian culture, flourishing during the Uruk Period, provided the fertile ground upon which the seeds of knowledge sprouted. It is within this cultural crucible that the earliest forms of writing, such as the wedge-shaped cuneiform script, emerged as a testament to the human quest for expression and communication.
As the sands of time continued to shift, the mantle of scientific exploration passed seamlessly into the Early Dynastic Period, spanning 2900-1750 BCE. The legacy of Mesopotamian scientific prowess endured, leaving an indelible imprint on subsequent civilizations that would gaze back in awe at the intellectual achievements of their forebears.
Navigating the Waves of Temporal Progress: Mesopotamian Technology Unearthed
Mesopotamian technology, intricately interwoven with the fabric of daily life, revealed itself as a marvel during the Uruk and Early Dynastic Periods. The Sumerians, in their pursuit of progress, crafted an array of technological marvels that elevated their society above contemporaneous civilizations.
In the realm of construction and urban planning, Mesopotamia showcased unparalleled sophistication. The city of Uruk itself, with its awe-inspiring ziggurats and intricate canal systems, stands as a testament to the ingenuity of ancient engineering. The wheel, an elemental invention that revolutionized transportation, found its genesis within these arid landscapes, forever altering the course of human mobility.
Agricultural innovations flourished, providing sustenance to burgeoning populations. The introduction of the plow, harnessing the strength of domesticated animals, marked a transformative moment in agricultural practices. This technological leap not only increased productivity but also laid the groundwork for the rise of complex societies dependent on surplus food production.
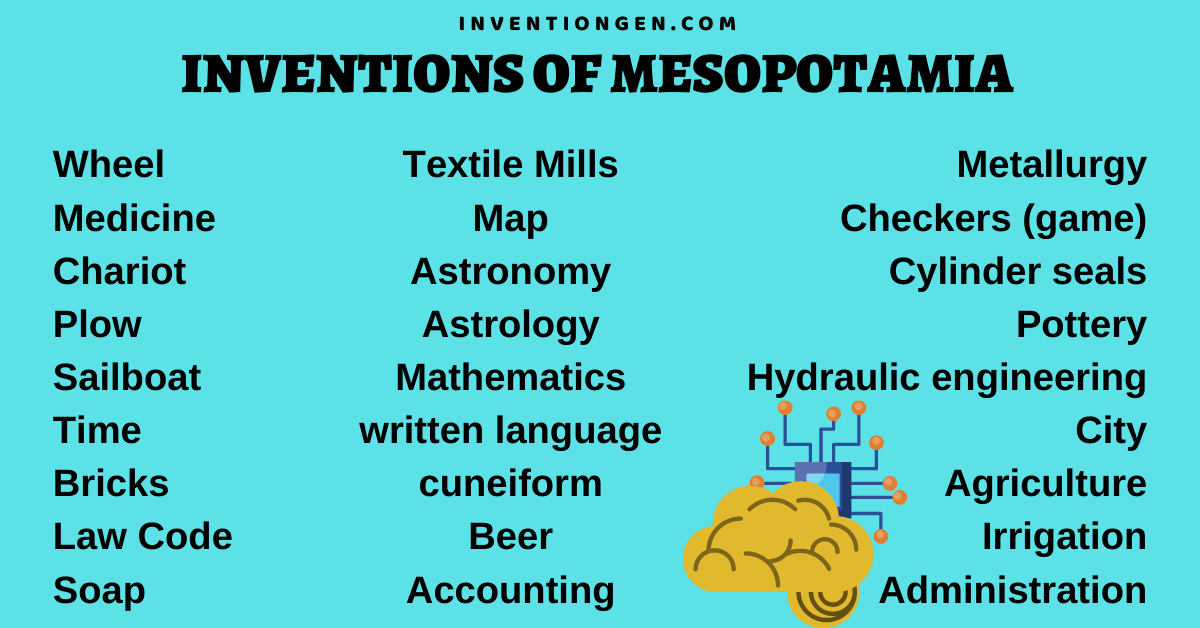
List of inventions of Mesopotamia
In retrospect, the radiant glow of Mesopotamian innovations continues to illuminate the corridors of our collective understanding. From the towering ziggurats reaching towards the heavens to the meticulous tablets bearing the weight of ancient wisdom, the legacy of Mesopotamia transcends temporal boundaries.
- Wheel
- Chariot
- Plow
- Sailboat
- Time
- Bricks
- Textile Mills
- Map
- Astronomy
- Astrology
- Mathematics
- Written language
- Cuneiform
- Metallurgy
- Decision-making
- Checkers (game)
- Cylinder seals
- Pottery
- Hydraulic engineering
- Agriculture
- Irrigation
- City
- Law Code
- Medicine
- Physicians
- Soap
- Administration
- Accounting
- Beer
Inventions of Mesopotamia
As we navigate the currents of history, the contributions of this cradle of civilization persist as beacons guiding us through the labyrinth of human progress. Mesopotamia, with its evergreen inventions, stands as a testament to the indomitable spirit of curiosity and ingenuity that defines our shared journey through time. Listed below are some of the greatest inventions of Mesopotamia:
1. Mesopotamian Timekeeping: Crafting the Foundations of Modern Chronology
In the fertile crescent of Mesopotamia, the challenge of synchronizing daily activities and marking the passage of seasons prompted the ingenious development of a temporal framework. Confronted with the intricate dance of the celestial bodies and the need for coordinated societal endeavors, Mesopotamians pioneered the division of time into units that resonate in contemporary clocks. Their groundbreaking contribution lies in the subdivision of hours into 60 minutes and minutes into 60 seconds, a legacy echoing through the ticking hands of every modern timepiece. This conceptual leap not only facilitated daily life but also laid the groundwork for the intricate chronology we navigate today.
2. Mesopotamian Chariots: Wheels of Progress in Transportation
As the pulse of civilization quickened, the burgeoning need to transport goods and people from one locale to another spurred an evolution in the means of conveyance. A pivotal chapter unfolded as humans learned to domesticate horses, bulls, and other beasts, leading to a subsequent breakthrough—the invention of the chariot. This four-wheeled marvel, born from the domestication of indispensable animals, emerged as the premier mode of personal transportation.
Mesopotamians, at the forefront of harnessing the potential of these majestic creatures, seamlessly integrated chariots into the tapestry of their daily lives. The chariot, with its multifaceted utility, transcended mere practicality, becoming a stalwart companion in warfare, a fixture in recreational pursuits, and an indispensable tool for everyday transportation.
3. Agricultural Triumphs in Mesopotamia: Sowing the Seeds of Civilization
In the cradle of civilization, Mesopotamian farmers emerged as architects of sustenance, cultivating a diverse array of crops such as wheat, barley, cucumbers, and an array of nutritious vegetables. Before the advent of the plow, these industrious tillers of the soil employed stone hoes to laboriously plow the land. The transformative force behind their agricultural prosperity lay in the strategic harnessing of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, which encircled Mesopotamia.
These life-giving waterways not only facilitated irrigation but also rendered farming infinitely more manageable and efficient. The marriage of agricultural prowess and hydraulic ingenuity resolved the dual challenges of sustenance and commerce, laying the groundwork for the flourishing Mesopotamian civilization.
4. Mesopotamian Stargazing: Navigating the Cosmos for Religious Endeavors
In the quest for a deeper understanding of the cosmos and driven by the imperative of religious rituals, Mesopotamians embarked on a celestial exploration that intertwined the realms of astrology and astronomy. Seeking guidance from the stars, they delved into the mysteries of celestial bodies, their movements, and configurations.
Astronomy, initially a pragmatic tool for religious events, eventually evolved into a profound discipline, laying the groundwork for the understanding of cosmic patterns that transcended the terrestrial confines. Mesopotamians, through their celestial pursuits, not only enriched their religious practices but also paved the way for future advancements in the study of the cosmos.
5. Mesopotamian Urbanization: Foundations of Societal Structure
In the crucible of Mesopotamia, the concept of urban civilization emerged as a symbol of aristocracy, reshaping the very fabric of societal existence. As the echoes of agricultural innovation reverberated, people began to coalesce in specific locations, marking the inception of urbanization. Agriculture, facilitating the sustenance of larger populations, laid the groundwork for settlements where people could thrive.
This confluence of factors gave rise to trade and the development of taxation systems, defining the social and economic dynamics of Mesopotamian society. The urbanization phenomenon, crystallizing notably during the Uruk period (4300–3100 BC), witnessed the construction of colossal walls surrounding cities, such as those attributed to King Gilgamesh. These walls, both literal and metaphorical, delineated the contours of burgeoning urban centers, becoming a testament to the enduring legacy of Mesopotamian societal structures.
6. Cuneiform Script: Crafting the Chronicle of Mesopotamian Civilization
In the annals of human communication, the Mesopotamians etched their mark with the advent of cuneiform script—a pioneering writing system that not only documented daily occurrences but also became a conduit for the transmission of knowledge and history. Evolving from simple pictographs, cuneiform symbols transformed into a sophisticated script by 2900 BC, reducing the vast array of visual representations to a streamlined repertoire of 600 words.
These symbols, initially resembling miniature depictions of objects like horses, metamorphosed into a language of record-keeping and storytelling. Scribes, the custodians of this intricate script, played a pivotal role in the preservation and dissemination of Mesopotamian history, casting the narrative of their civilization in the enduring clay tablets adorned with cuneiform inscriptions.
7. Mesopotamian Law Code: Crafting the Blueprint for Civilization
In the tapestry of Mesopotamian civilization, the establishment of a comprehensive law code emerged as a pivotal milestone, laying the groundwork for a systematic and civilized society. Formulated to curb crimes and instill loyalty among citizens, this intricate network of laws, orders, rules, regulations, policies, and handbooks served as the bedrock of societal governance.
Designed to navigate the complexities of human interactions, the Mesopotamian legal system contributed to the evolution of a structured and orderly nation. As a testament to the importance placed on justice and governance, these laws became a guiding force, shaping the behaviors and responsibilities of individuals within the sophisticated framework of Mesopotamian society.
8. Copper Fabrication: Forging the Blades of Mesopotamian Might
The mastery of metallurgy in Mesopotamia reached its zenith with the fabrication of copper, marking a transformative chapter in the realms of warfare and metalworking. Around 5000 BC, copper emerged as the first metal to be smelted from its ore, laying the groundwork for subsequent advancements in metallurgy. By approximately 4000 BC, Mesopotamians had elevated their metalworking proficiency to the point of forging basic metals in molds, a testament to their burgeoning expertise.
The true pinnacle of their metallurgical prowess, however, materialized around 3500 BC with the alloying of copper and tin to birth bronze—an innovation that revolutionized weaponry and craftsmanship. This alloyed metal not only fortified their armaments but also became a hallmark of Mesopotamian technological achievement, cementing their reputation as adept metalworkers and warriors.
9. Mesopotamian Soap: Aromatic Elegance and Hygiene Innovation
Around 2800 BC, Mesopotamians introduced a revolutionary concept that would transform the realms of personal care and hygiene—a soap-like substance. This fragrant marvel not only served as a cleansing agent but also imbued the art of beautification with a newfound fervor. Mesopotamian society, already marked by advancements in various domains, now embraced a fragrant embrace of cleanliness and aesthetic appeal. The introduction of this soap marked a cultural milestone, intertwining the notions of beauty and hygiene in a scented dance that reverberated through the millennia.

10. Mesopotamian Beer Culture: A Warm Embrace in Cold Times
In the vibrant tapestry of Mesopotamian cities, the innately social nature of humanity found expression in the numerous inns, taverns, and pubs that dotted the urban landscape. Beyond mere establishments, these venues became communal spaces where people congregated to share camaraderie, indulge in delectable meals, and, perhaps most notably, savor a drink or two. The libations of choice in these convivial settings invariably leaned towards beers, a diverse array that included golden, dark, sweet dark, red, and strained varieties. Beyond mere refreshment, beer in Mesopotamian culture became a source of warmth and conviviality, offering a comforting embrace, particularly during colder times.
11. Mesopotamian Bricks: The Foundation of a Civilization’s Ascent
The ascent of Mesopotamia to the pinnacle of civilization was not merely an abstract concept; it was meticulously crafted, brick by brick, in a testament to their innovative prowess. The Mesopotamians, envisioning the grandeur of cities and the flourishing tapestry of urbanization, ushered in a groundbreaking invention—the use of bricks. This ingenious construction material became the cornerstone upon which the Mesopotamians built the world’s most formidable civilization at the time.
Crafted from clay and subsequently fired, these bricks assumed various shapes, sizes, and designs, enabling the architects of Mesopotamia to fashion structures that reached the heavens. The utilization of bricks not only facilitated the physical construction of cities but also symbolized the indomitable spirit of Mesopotamian innovation—a testament to their enduring legacy as architects of an unparalleled civilization.
12. Mesopotamian Board Games: Pastime Pleasures Amidst Mugs and Laughter
As the Mesopotamians reveled in the camaraderie of inns and taverns, they ingeniously intertwined leisure activities with their sociable gatherings. To complement the conviviality of beer-filled moments, a plethora of entertainment emerged. Mesopotamians, in their pursuit of enjoyment, crafted drinking games, orchestrated lively dance and musical performances, and engaged in the spirited play of board games.
These diversions, woven into the fabric of social pastime, provided a well-rounded experience for those seeking respite from the rigors of daily life. The clinking of mugs, laughter, and the strategic moves on board game surfaces became integral components of Mesopotamian leisure, fostering an atmosphere of joy and relaxation in the heart of their cities.
13. Administrative Brilliance: Mesopotamian Pioneers in Systematic Governance
In the intricate tapestry of Mesopotamian society, the mastery of administration and accounting emerged as hallmarks of their systematic governance. Surpassing their contemporaries, Mesopotamians showcased an administrative acumen that laid the foundation for efficient clerical activities. The hierarchical administrative structure, finely tuned and organized, facilitated the coordination of tasks and responsibilities, ensuring the smooth functioning of the nascent bureaucracy.
Simultaneously, their prowess in accounting transcended mere record-keeping, evolving into a sophisticated system that underpinned the dynamics of business and exchange. Mesopotamians, with their adeptness in administration and accounting, charted a course of systematic governance that resonated through the corridors of time, leaving an indelible mark on the annals of ancient administrative brilliance.
14. Mesopotamian Literature: Crafting Artistry with Cuneiform
In the tapestry of Mesopotamian civilization, literature ascended to new artistic heights, unveiling a rich narrative woven through the intricate strokes of cuneiform script. Originating in the latter half of the 4th millennium BC, cuneiform, meaning ‘wedge form,’ became the instrument through which the Mesopotamians expressed their intellectual and creative endeavors. Invented by the Sumerians, this script transcended mere record-keeping, evolving into a versatile medium for a myriad of expressions.
Mesopotamians, through their adept use of cuneiform, not only documented historical records but also produced literary masterpieces, depicted articles, painted images, developed laws, researched medicine, explored astronomy, and propagated education. The epic of Gilgamesh, a monumental literary achievement, stands as a testament to the artistic zenith achieved by Mesopotamian culture through the amalgamation of art, writing, and cultural expression.
15. Mesopotamian Medicine: Healing Arts Beyond Imagination
In the realm of health and well-being, Mesopotamians stood as pioneers, advancing the field of medicine beyond contemporary imagination. The vibrancy of their medical practices was marked by the presence of two distinct categories of healers. The Asu, akin to modern medical practitioners, prescribed various therapies for illnesses and injuries, relying on empirical knowledge and practical treatments. In parallel, the Asipu, a holistic healer, delved into the realms of magical spells, amulets, and incantations, seeking healing through spiritual and mystical channels.
Remarkably, both these professionals were regarded with equal respect and often collaborated, creating a unique synergy between empirical and mystical approaches to healthcare. This harmonious coexistence of medical traditions exemplifies the comprehensive nature of Mesopotamian medical practices, shaping a narrative of health and healing that resonates through the annals of ancient history.
16. Mesopotamian Technological Renaissance: Forging the Foundations of Civilization
In the crucible of Mesopotamia, technological innovation burgeoned, bestowing upon the world an array of advancements that defined the very essence of civilization. The Mesopotamian people, bestowed with an ingenious spirit, birthed technologies encompassing metal and copperworking, glass and lamp making, textile weaving, flood control, water storage, and irrigation. As pioneers of the Bronze Age, they manifested their metallurgical prowess by adorning palaces with kilograms of precious metals—copper, bronze, and gold.
In the realm of warfare, Mesopotamians showcased their mastery in metallurgy by transitioning from copper and bronze to the formidable iron. These technological strides not only elevated their society but also manifested in the creation of sophisticated armaments, including swords, daggers, spears, and maces. Mesopotamia, standing at the vanguard of technological innovation, sculpted a legacy that reverberates through the echoes of time as a testament to their civilized ingenuity.
17. Mesopotamian Cartography: Navigating the Ancient World with Clay Maps
The innovative spirit of Mesopotamians extended to the realm of exploration with the invention of maps—a critical milestone in their pursuit of knowledge. Among the tangible relics of this cartographic ingenuity is a clay map depicting the Akkadian region of Mesopotamia. While the coverage of this map is modest, its significance resonates through its multifaceted applications. Serving as a city map for military campaigns, hunting expeditions, and trade ventures, this clay map represents one of the greatest inventions of Mesopotamia.
It not only facilitated practical exploration but also laid the foundation for a systematic approach to understanding and navigating the landscape. In the hands of Mesopotamian cartographers, clay became a canvas for charting the course of exploration and knowledge acquisition.
18. Mesopotamian Sailboats: Navigating Waters, Transforming Trade
In a landscape where land transportation posed formidable challenges and consumed vast amounts of time, the inventive spirit of Mesopotamians sought solace on the waters. The sailboat emerged as a transformative innovation, etching its place among the great inventions of Mesopotamia. The initial sailboat, though characterized by a simple and primitive design, ushered in a new era of mobility, particularly in the realm of naval systems.
A crucial breakthrough for commerce and trade, the sailboat enabled efficient exploration of waterways, notably the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. Its humble origins in fishing expeditions soon expanded to facilitate the discovery of distant territories, marking a paradigm shift in Mesopotamian transportation and laying the foundation for maritime endeavors that would shape the course of history.
19. The Wheel: Revolutionizing Mobility, Craftsmanship, and Labor
In the annals of technological innovation, the invention of the wheel stands as a pivotal moment, unfolding around 3500 BC in the hands of skilled potters. Initially conceived as a potter’s wheel, this humble invention rippled through the fabric of Mesopotamian society, triggering a revolution in the realms of speed, effort, and time.
While initially a symbol of opulence for the affluent, the wheel swiftly transcended its exclusivity, finding utility in diverse domains. Beyond its role in transportation for the privileged few, the wheel became a linchpin in irrigation systems, revolutionized pottery making, and facilitated the arduous task of milling. This seemingly simple yet ingenious invention, born from the hands of potters, became a cornerstone of progress, propelling Mesopotamia into a new era of efficiency and productivity.
20. Agricultural Revolution: Mesopotamian Mastery of the Plow
In the fertile crescent of Mesopotamia, where the cradle of civilization flourished, the symbiotic relationship between humans and animals reached new heights with the domestication of oxen. Harnessing the strength of these animals marked a paradigm shift in daily life, leading to the development of the first plow, aptly named the “ard.” Mesopotamians, recognizing the transformative potential of this agricultural implement, ushered in an era of unparalleled agricultural productivity.
The plow, cutting through the fertile soil, became the linchpin of Mesopotamian agriculture, cultivating lands and laying the groundwork for bountiful harvests that fueled the sustenance of their growing civilization. In the wake of the ard’s introduction, the landscape of Mesopotamia witnessed a verdant surge, as the agricultural revolution unfurled its tendrils, weaving prosperity into the fabric of everyday existence. Buy Textbooks. Sell Textbooks. eTextbooks. Most Used Textbooks On the Planet. 10 million books. 50% Cash Back Books. FREE Shipping
21. Mesopotamian Mathematics: The Bedrock of Practical Calculation
In the bustling commerce and burgeoning civilization of Mesopotamia, the necessity for precise calculations permeated every facet of daily life. From the exchange of goods to the cultivation of crops and the construction of structures, a robust numerical system became imperative. Mesopotamians, in response to this demand, ingeniously devised a counting system, laying the foundation for practical arithmetic. The exagesimal system, rooted in the base-60 concept, permeated their numerical landscape. This system not only facilitated the tallying of products but also found its expression in the 360-degree circle, mirroring the twelve-month cycle of the year.
Additionally, the invention of 12 knuckles and 5 fingers served as a practical embodiment of this numerical system, offering a tangible means for counting and calculation. Furthermore, Mesopotamians pioneered the concept of zero, a mathematical placeholder that would later weave itself into the fabric of numerical notation, though debates persist about its origin, tracing it to Babylonians or Indians. Mesopotamian mathematics, a cornerstone of their flourishing civilization, not only facilitated trade but also laid the groundwork for numerical systems that transcend millennia.
More Interesting Articles
- 7 Easy Steps to Have the License for A New Invention
- 45 Cool Future Inventions – Sci-Fi, Prediction, or Reality?
- 120 World’s Greatest Inventions of the Last 100 Years
- Automation Challenges Factors and How to Overcome
- 16 Digital Transformation Trends in 2024 and Beyond
- 25 Predictions of Bad Inventions in the Future
- 35 Most Important Evergreen Inventions of All Time
- 50 Greatest Inventions of the 21st Century
- 40 Futuristic Inventions – A Prediction on Future Technologies
- 10 Excellent Inventions of the 2000s Timeline
- 30 Remarkable Inventions Made from 2000 to 2019
- 10 Steps to Learn How to Make An Invention
- 10 Popular Inventions in the Golden 1970s
- 20 Examples of Artificial Intelligence in Daily Life
- 30 Interesting Scientific Inventions and Discoveries
- 70 Inventions Made in America – Great US Inventions
- 35 Inventions Made by Accident – Accidental Inventions
- Permanent Artificial Heart – History | Mechanism | Options
- 10 Top Inventions in the 80s That Gained Huge Popularity
- 10 Invention Examples that Became Popular in the 90s